The data and insights provided by our weather and Earth science technologies are shaping the future of forecasting to help save lives and improve resilience.
Our advancements in technology are revolutionizing the way we monitor the weather, environment, and solar activity on and around Earth. Sophisticated satellites and sensors we've developed provide real-time data on atmospheric conditions, ocean temperatures and solar emissions, delivering unprecedented insight into our planet’s complex systems and the near-space environment.
By analyzing data from Earth-observing satellites and instruments developed by our engineers, we can help scientists, meteorologists and emergency managers identify patterns, track anomalies and predict weather events with improved accuracy. These technologies also track solar phenomena such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares that drive space weather, which can disrupt power grids and communication networks on Earth and satellites in space.
In addition to 60+ years of heritage building satellites and complex instruments, we also develop advanced intelligence products that enable improved decision-making for users in industries like agriculture, insurance and defense.
Discover Our Weather Forecasting and Satellite Technologies
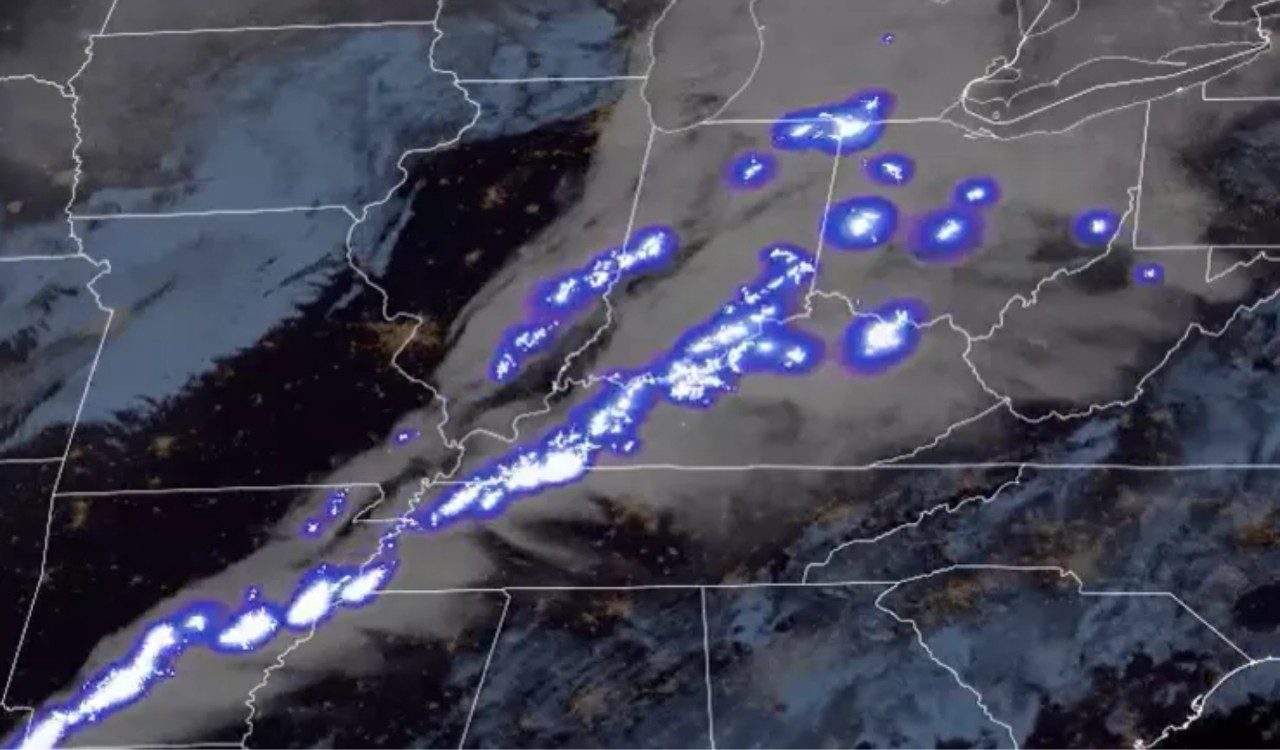
For decades, NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellites (GOES) have been the foundation for reliable weather forecasting. With the recently completed GOES-R series, built by Lockheed Martin, we reached an entirely new level of precision and timeliness. These advanced satellites deliver critical data across atmospheric, hydrologic, oceanic, climatic, solar and space domains, revolutionizing how environmental phenomena are detected and monitored.
With advancements in imagery and data solutions, GOES-R satellites can help predict and analyze weather and environmental conditions both on Earth and in space. This capability improves the accuracy and effectiveness of split-second decisions that protect lives, safeguard property and support economic resilience—proof of the value of sustained technological innovation.
GeoXO builds on the success of the GOES-R series, expanding critical weather observations to include new insights into our oceans and air quality. With advanced capabilities, GeoXO will enhance weather forecasting and address emerging environmental challenges, strengthening national preparedness. These satellites will provide groundbreaking data, from real-time atmospheric mapping to the first geostationary views of coastal ecosystems and air pollution.
Planned for launch in the early 2030s, GeoXO will serve through the 2050s, powered by Lockheed Martin’s LM2100™ satellite bus and SmartSat™ technology. These innovations will ensure adaptability as users’ needs evolve, making GeoXO a vital tool for protecting lives, property and the planet for decades to come.

LMX: the Next-Generation Lightning Mapper for GeoXO
GeoXO's Lightning Mapper (LMX) builds on the success of the Lockheed Martin-built Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) on the GOES-R satellites, offering finer spatial resolution, faster imaging and expanded coverage—including Alaska.
These advanced lightning data will enhance storm analysis and prediction, aiding in the detection of tornado-producing storms and improving hurricane intensity estimates. It will also support wildfire ignition detection, lightning hazard identification and aviation threat avoidance.
LMX will be developed at Lockheed Martin’s Sunnyvale, California facility and represents a leap forward in geostationary lightning mapping, providing critical insights to protect lives and property in the face of severe weather.
The Lockheed Martin Environmental Intelligence team is leveraging our expertise in remote sensing, artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) and data science to deliver customized decision support tools for end users across public and private sectors. We aim to help customers worldwide make better sense of their data and, through the use of trusted systems and analysis, better understand, predict and respond to the increasing environmental uncertainty in the world.






